This article on the Gutenberg Migration Guide was originally published by Torque Magazine, and is reproduced here with permission.
Love it or loathe it, Gutenberg is here to stay. As such, getting your WordPress themes and plugins to work with the new editor should be a primary concern. Truth be told, if you’re only just thinking about this aspect now, you’re cutting things pretty close. However, there’s still enough time to prepare your products, especially with some third-party help.
Daniel Bachhuber’s Gutenberg-related projects have been featured on the Torque blog previously, and this is another one that warrants attention. Tweaking your plugins to be compatible with Gutenberg could prove to be a tricky task, but the Gutenberg Migration Guide should help you make the switch. It’s a handy reference guide for comparing customization points between WordPress’ classic editor and Gutenberg.
In this post, we’ll look at the project as a whole and discuss how it works. Then we’ll talk about how to make sure your plugins and themes are Gutenberg-ready. Let’s get started!
The Current State of the Gutenberg Editor
We’ve talked about Gutenberg’s history on the Torque blog a lot, so we won’t go into too much detail here. However, to offer some background context, Gutenberg is eventually going to be WordPress’ new default editor. It will be replacing the TinyMCE version that is currently in place. While Gutenberg is now out of beta, we’re still waiting for the plugin to be merged into the core platform.
However, despite the sound reasoning behind Gutenberg’s functionality, many have been left unimpressed by the lack of polish in the editor so far. This assessment may be somewhat harsh, considering the project’s current status. In any case, the high level of criticism has resulted in a lack of movement from many WordPress developers, especially when it comes to getting their products up to standard.
This hasn’t stopped some savvy developers from trying to capture the early adopter market, however. For example, the very popular Elementor Pro page builder now includes a number of Gutenberg-compatible ‘blocks’. Other developers are also beginning to include this functionality as a standard feature:
The fact that we’re finally seeing Gutenberg-related features appearing in commercial themes should bring the situation into perspective. In other words, some developers have been working on their Gutenberg solutions for a while. Now, they’re now beginning to offer them to the public.
If you’ve not yet begun to do the same, you’ll likely need some help getting started. Fortunately, there’s a great initiative that offers just that.
Introducing the Gutenberg Migration Guide
Having some support while migrating your functionality over to Gutenberg is likely going to be welcome to many developers. For that reason, Daniel Bachhuber – who has become a focal point for Gutenberg-related initiatives of late – has created the Gutenberg Migration Guide.
This is a resource to help developers port their TinyMCE-centric plugins and themes to the new editor. It includes plenty of screenshots, and handy references to the Gutenberg Developer’s Handbook. You can think of it as Gutenberg’s own ‘Codex’, although it’s not classed as an official part of the WordPress Codex.
This guide also includes a brief overview listing every TinyMCE editor customization point with a Gutenberg equivalent. Plus, it covers all impacted hooks and classic editor features. This will obviously be a vital go-to resource when you’re trying to find solutions for porting functionality over to Gutenberg.
How You Can Help the Gutenberg Migration Project Succeed
As outlined on a Make WordPress blog post towards the end of April, Daniel is looking to crowdsource this project, rather than remain the sole contributor. However, despite the plethora of components that make up the new editor, additional contributions have been sparse:

Therefore, especially given the high value of the project, more contributors are required to help fill out the guide. To begin contributing, you can simply send a pull request as usual, which will then be approved and merged into the guide proper. You can also suggest a new hook (or ask a question) by opening a GitHub issue.
How to Use the Gutenberg Migration Guide to Deliver Modern WordPress Plugins
Actually using the Gutenberg Migration Guide is an absolute breeze, mainly due to its highly-organized layout:
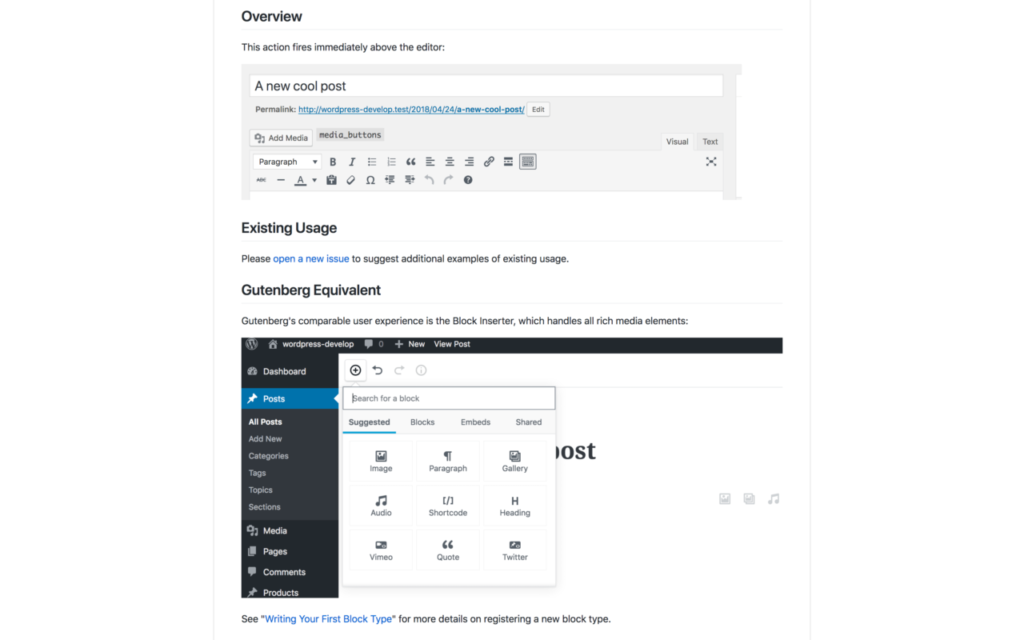
You’ll find a reference to the relevant TinyMCE editor action or filter at the top of each page, and then a generic example of where it’s used within WordPress. Next, you’ll find real-world examples of how the hook is used. This is one area where the project needs more contributions. There are many plugins that will add their own functionality to the editor, which need to be documented.
Below that, you’ll find a screenshot of the equivalent hook within Gutenberg. This will be accompanied by a brief explanation of where you can find that hook, along with any esoteric information regarding its use. Finally, there’s a handy reference to the Gutenberg Developer’s Handbook, to help you along if you require more information.
Overall, this is a very useful reference guide for Gutenberg developers, and should be bookmarked while you’re going through the migration process. In our opinion, the first parts you should check out are the aspects that haven’t yet made the switch to Gutenberg. For example, there are a number of edit_form actions that are no longer compatible within Gutenberg. Depending on your theme or plugin’s functionality, this could require a comprehensive workaround.
Finally, two other classic editor features that haven’t been incorporated into Gutenberg are the Screen Options tab and the unofficial Custom Post Status feature. The former is likely to be more concerning for many developers, as that was a ‘power’ feature a lot of WordPress users found helpful.
Making sure your themes and plugins can adapt to both editors despite these changes is absolutely vital. As you’ve seen, the Gutenberg Migration Guide is what will get you there.
Conclusion
Gutenberg has its detractors, but each beta update is bringing more to the party. The new editor is slowly becoming a powerful method for creating WordPress layouts, which is great news for both end users and developers.
What’s more, the Gutenberg Migration Guide from Daniel Bachhuber can be an excellent resource for those needing to adapt their own projects quickly. It’s incredibly simple to use as-is, but still needs assistance from the WordPress community to reach its full potential. To help out, you can send a pull request, open a GitHub issue, or even offer your own real-world examples of Gutenberg equivalents to the TinyMCE editor’s functionality.
Frequently Asked Questions about Modern WordPress Plugins with the Gutenberg Migration Guide
What is Gutenberg in WordPress?
Gutenberg is a new editor introduced in WordPress 5.0. It replaces the previous TinyMCE editor and offers a more visual, block-based approach to content creation. Each piece of content, whether it’s a paragraph, image, or video, is a block that you can manipulate individually, offering more flexibility and control over your content layout.
How do I migrate to Gutenberg?
Migrating to Gutenberg involves installing and activating the Gutenberg plugin or updating to WordPress 5.0 or later. Once activated, Gutenberg will replace the default editor. It’s recommended to backup your site before making the switch and to test the new editor on a staging site first.
What are Gutenberg blocks?
Gutenberg blocks are individual elements that you use to build your content in the Gutenberg editor. There are blocks for all types of content, including paragraphs, images, videos, columns, and more. Each block can be customized and arranged to create unique layouts.
How do I add new blocks to Gutenberg?
You can add new blocks to Gutenberg by clicking on the plus (+) icon in the editor. This will open a menu where you can search for and select the type of block you want to add. There are also plugins available that add additional blocks to Gutenberg.
Can I still use my old plugins with Gutenberg?
Yes, most existing WordPress plugins should work with Gutenberg. However, some plugins may not be compatible and could cause issues. It’s recommended to test all plugins with Gutenberg on a staging site before using them on your live site.
What are some recommended Gutenberg block plugins?
There are many great Gutenberg block plugins available. Some popular ones include Advanced Gutenberg, Stackable, and Atomic Blocks. These plugins add a variety of additional blocks to Gutenberg, giving you even more options for your content.
How do I customize Gutenberg blocks?
Gutenberg blocks can be customized using the block settings in the editor. These settings allow you to change the block’s appearance, layout, and other attributes. Some blocks also support additional customizations through CSS.
Can I revert back to the old editor if I don’t like Gutenberg?
Yes, if you prefer the old editor, you can install and activate the Classic Editor plugin. This will disable Gutenberg and restore the previous TinyMCE editor.
Is Gutenberg SEO-friendly?
Yes, Gutenberg is designed to be SEO-friendly. The block-based structure makes it easier to create clean, structured content that’s easy for search engines to understand. However, like with any content, it’s important to follow best practices for SEO.
How do I learn to use Gutenberg?
There are many resources available to help you learn Gutenberg. WordPress offers a tutorial in the Gutenberg editor, and there are numerous online tutorials and guides available. Practice and experimentation are also great ways to learn the ins and outs of the new editor.
 Tom Rankin
Tom RankinTom Rankin is a key member of WordCandy, a musician, photographer, vegan, beard owner, and (very) amateur coder. When he's not doing any of these things, he's likely sleeping.